Animal tissue is classified into four types that are epithelial tissue, muscular tissue, connective tissue and nervous tissue.
Epithelial tissue

Animal Tissue : Epithelial Tissue
Cells in epithelial tissues are arranged in tiles format i.e. are tightly pack such that there are no intercellular spaces in it. Epithelial tissues are present in skin, respiratory tract, in lungs alveoli, in kidney tubules, etc. Also, There is presence of basement membrane with separates epithelial tissues from other tissues.
- Squamous epithelium: Cells in squamous epithelium are thin, flat and forms a thin lining. These are present in lining of oesophagus, mouth, blood vessels, lung alveoli, skin, etc. Moreover, this animal tissue transports material through selectively permeable membrane. If present in number of layers, this tissue is known as stratified squamous epithelium.
- Columnar epithelium: In animal tissues, columnar epithelium shows column like structure. These are present in the area where absorption and secretion occurs, like inner lining of intestine. Moreover, in respiratory tract, columnar epithelium contains cilia, which helps particles to move in right direction.
- Cuboidal epithelium: In animal tissues, cuboidal epithelium has cube like structures. It is present in lining of kidney tubules. Also, this tissue undergo modification and forms a gland, which gives out substances on the surface of the tissues, hence, are known as glandular epithelium.
Muscular tissue
Humans and animals perform various muscular work like running, walking, due to presence of muscular tissue. This animal tissue, contains contractile protein, which contracts and relax, thereby providing motion. In particular, muscle tissue or muscle is made up of muscle fibres having elongated cells. This animal tissue is of three types striated muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscle.

Animal Tissue: Muscular Tissue
- Striated muscle: It is cylindrical, elongated, unbranched and multinucleated and show alternate light dark bands i.e. striations. Specifically, these muscles are located in limbs. They are responsible for voluntary movements.
- Smooth muscle: Smooth muscles are elongated, pointed at both ends making spindle shape having single nucleus. Particularly, smooth muscles lack striations. These are found in alimentary canal, iris of eye, in ureters, in bronchi of lungs. As a result, they are responsible for involuntary movements.
- Cardiac muscle: In animal tissues this type of muscle is elongated, cylindrical, branched containing single nucleus. These muscles are present in heart, and performs contractions and relaxation. Hence, are known as cardiac muscles. Also, these, muscles are involuntary in nature
Connective Tissue
This animal tissue is classified into blood, bone, ligament, tendon, areolar tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage tissue.

Animal Tissue: Connective Tissue
- Blood: It is made up of plasma, RBC’s i.e Red blood corpuscles, WBC’s i.e. White blood corpuscles and platelets. Blood connect all parts by of body by providing nutrients, exchanging materials, hence, it is a connective tissue.
- Bone: Bone is also a type of connective animal tissue. Cells in bone are fixed in matrix. It is composed of calcium and phosphorous. Therefore, bone tissues are hard and forms body structure, also, white blood corpuscles are produced in bone.
- Ligaments are the connective tissue that are flexible strong, contains less matrix. In particular, ligaments join two or more bones
- Tendons: It is fibrous, strong, less flexible. In particular, tendons joins muscles with bones.
- Cartilage: Among animal tissues, cartilage is the connective tissue in which cells are fixed firmly in the matrix made up of sugar and proteins.
- Areolar tissue: It is composed of reticular fibres, fibroblast, collagen fibres, plasma cell, etc. Moreover, it binds skin and muscles and also provides support to internal organs.
- Adipose tissue: It is also known as fatty tissue. Adipose tissue is composed of adipocytes or fat cells. Hence, these cells stores energy in form of fat. It is present under skin it provides insulation to body and also acts as protective covering internal organs.
Nervous Tissue
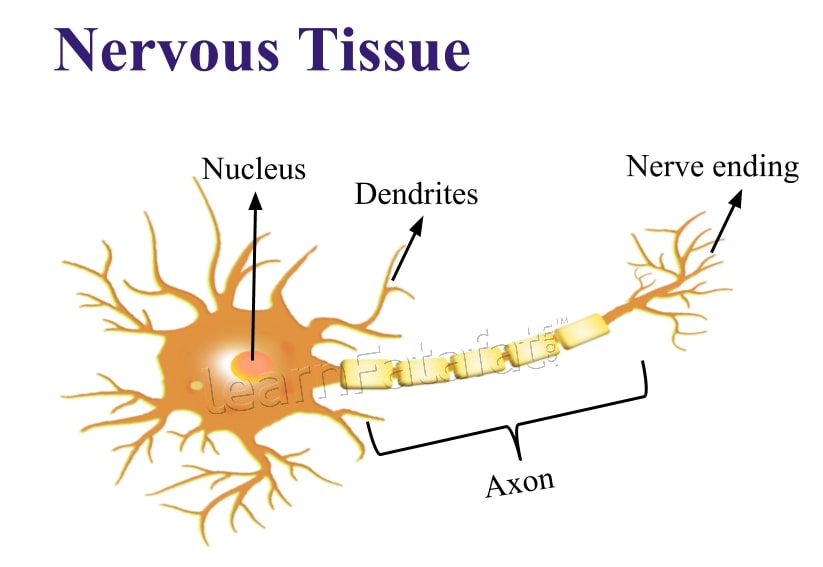
Animal Tissue: NErvous Tissue
Nervous tissue consist of nerve cells or neurons. Nerve cell consist of nucleus and cytoplasm. Long part of nerve cell is called axon and branched outgrowth along the nucleus are dendrites. Brain, spinal cord, nerves are made of nerve tissue. In animal tissue, nervous tissue play an important role of performing appropriate action. Therefore, it prevents us from accidents.
Keywords: CBSE Class 9 Animal tissue, Epithelial tissue, Muscular tissue, Connective tissue, Nervous tissue, Blood, Bone, Cartilage, Tendon, Ligament, Areolar tissue, Adipose tissue, Fatty tissue, Adipocytes
Related articles
Structure and Functions of Plasma Membrane in a Cell
Structure and functions of human eye
Meristematic Tissue in Plants
Working of Human Digestive System
Simple permanent tissue in plants


What is the difference between animal tissues and plant tissues?
Hi,
Here are few differences between animal tissue and plant tissue