NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
LearnFatafat offers free NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues. Chapter covers the topics like Introduction to Tissues, Plant Tissue : Simple Permanent Tissue, Plant Tissue : Complex Permanent Tissue, Animal tissues : Epithelial Tissues and Muscular Tissues, Animal Tissues : Connective Tissue and Nervous Tissue. Check video lessons, notes and MCQ quizzes for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues click here to buy.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
1. Define the term “tissue”.
Answer: Group of cell having similar structure performing particular function is called tissue.
2. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer: Xylem is formed from following cell –
- Tracheids
- Vessels
- Xylem parenchyma
- Xylem fibres
3. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
| Simple Tissues | Complex Tissues |
|---|---|
| Simple tissues has only one type of cells | Complex tissues are made up of two or more types of cell |
| All cells perform same similar functions and has similar structures | Different cells perform different functions |
| Simple tissues are parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma | Complex tissues in plants are xylem and phloem. |
4. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer:
| Parenchyma | Collenchyma | Sclerenchyma | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intercellular spaces | Large | Less | No spaces |
| Cell (Dead / Alive) | Alive | Alive | Dead |
| Cell wall | Thin | Irregularly thick | Thick |
| Functions |
|
|
|
5. What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer: Following are the functions of stomata-
- Exchange of gases oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Loss of excess of water through plants by the process of transpiration.
6. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:

7. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer: Cardiac muscles are responsible for contraction and relaxation of heart.
8. Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:
| Muscle Type | Structure | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Striated muscle |
|
Present in limbs | Allows voluntary movements |
| Smooth muscle |
|
Present in alimentary canal, iris of eye, in ureter, in bronchi of lungs | Allows involuntary movements |
| Cardiac muscle |
|
Heart | Allows continuous contraction and relaxation |
9. Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Answer:
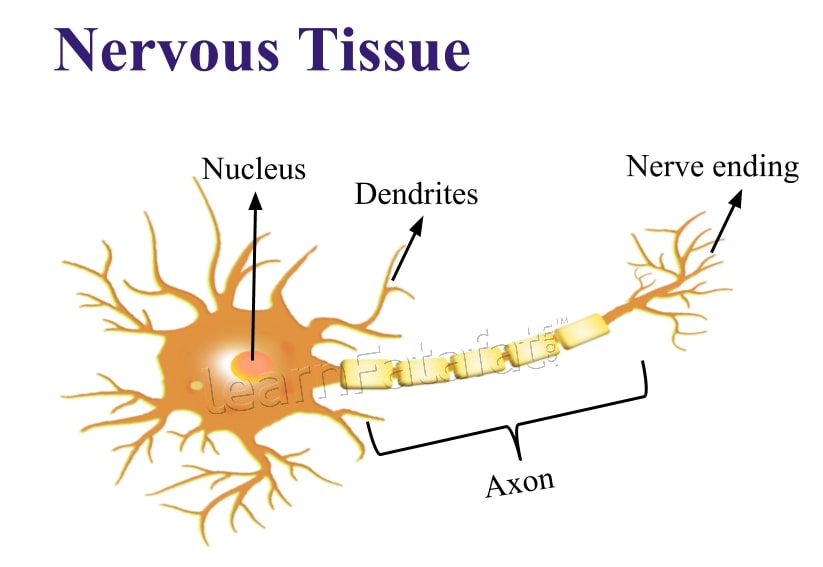 Animal Tissue: NErvous Tissue[/caption]
Animal Tissue: NErvous Tissue[/caption]
10. Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
Answer: Epithelial tissue
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
Answer: Tendons
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
Answer: Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
Answer: Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
Answer: Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer: Nervous tissue
11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
- Skin – Squamous epithelial tissue
- Bark of tree – Simple permanent tissue
- Bone – Connective tissue
- Lining of kidney tubule – Cuboidal epithelial tissue
- Vascular bundle – Complex permanent tissue
12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer: Parenchyma is present in leaves, flowers and fruits of the plant.
13. What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer: Epidermis is responsible for –
- Protection of plant body from external agents
- Protects plant body from mechanical injury
- Allows exchange of gases through stomata
14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer: Cork or bark of tree is its outer protective layer. Cork is made up of dead cells. It protects plants from higher temperatures, winds, mechanical injuries, etc.
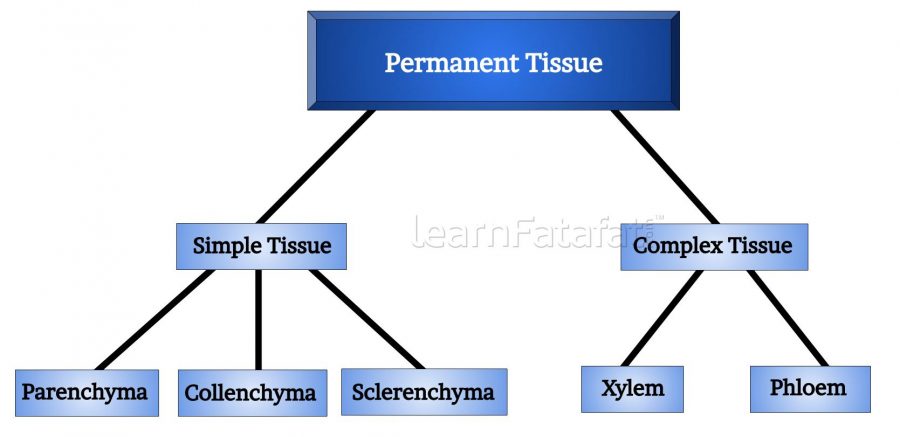
15. Complete the following chart:

Answer:
Check other lessons NCERT Solutions for Class 9
Download free NCERT textbook class 9 Science – Chapter 6 Tissues
CBSE Class 9
Access Class 9 video lessons online (internet required) or offline(internet not required) in SD Card, Pendrive, DVD, Tablet.
Chapter 6 – Tissues






